According to the National Association of Fire Equipment Distributors’ report The Effectiveness of Portable Fire Extinguishers:
“Time and time again, portable fire extinguishers have proven to be the most effective means of defense against fires of limited size. The National Association of Fire Equipment Distributors has conducted four extensive surveys since 1976 to measure the effectiveness of fire extinguishers … and the data collected during these surveys shows that portable fire extinguishers were effective in extinguishing fires 95% of the time.”
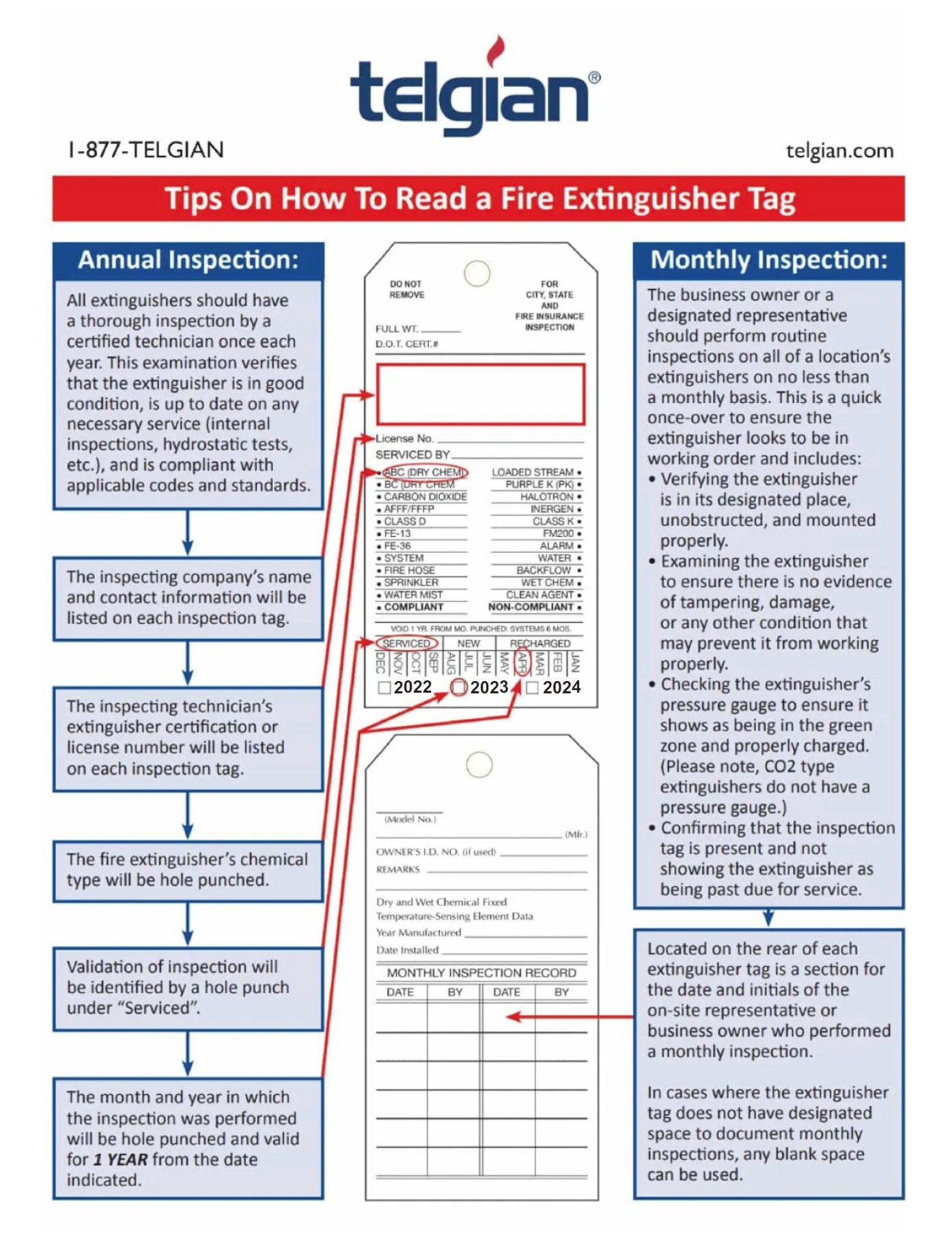
A fire extinguisher can only put out a fire, however, if it is in proper working condition, which is why conducting a fire extinguisher inspection is vital. And, the first step is learning how to read a fire extinguisher tag.
How to Properly Read Fire Extinguisher Tags
The tag is where you will find everything you need to know about your extinguisher, including the serial number, model number or other identifying information. Some fire extinguishers have multiple tags, including one that lists its expiration date and another noting the fire extinguisher’s status. The latter is a status or cylinder tag, and it’s usually yellow. Each state has different requirements regarding what the status tag should list. All recorded information is essential for maintaining the efficacy of your fire extinguisher — never remove or mark on the tag unless authorized to do so.
The status tag provides all the essential information you need to know about your fire extinguisher, including:
- The name of the company and person who last inspected the fire extinguisher.
- The date of the last inspection.
- The license number or certification of the inspecting technician.
- The fire extinguisher’s chemical type. The type of chemical used in that fire extinguisher will be hole punched.
- Validation of inspection with a hole punch under “serviced.”
- The month and year when the last inspection was performed.
At the bottom of each fire extinguisher status tag, it will read either “Serviced, New, Recharged.” This descriptor refers to the active status of your extinguisher. Please note that some extinguisher models may report this condition on a gauge, rather than a label.
How to Read a Fire Extinguisher Expiration Date
You can tell when a fire extinguisher expires by looking at the year and month punched on the tag. The extinguisher expires one year after the date indicated on the tag. The expiration date can be found at the bottom of the fire extinguisher tag.
Fire Extinguisher Class
On the tag, you will find each fire extinguisher is either Class A, Class B, Class C, Class D, Class K or a combination of classes.
These classifications refer to the type of fires your extinguisher can put out.
- Class A: These extinguishers are suitable for common combustibles, including wood, paper, rubber, cloth and several types of plastics.
- Class B: These extinguishers help dissolve fires caused by most flammable liquids, such as gasoline and alcohol, and you should use them carefully.
- Class C: These extinguishers refer to fires caused by energized electrical equipment.
- Class D: These extinguishers can help combat fires related to combustible metals, and you should use them carefully to avoid worsening the fire.
- Class K: You will often find these extinguishers in commercial kitchens, as they help treat cooking oil-based fires.
- Combination classes: Extinguisher labels list combination classes as “Class ABC,” “Class DC” or something similar. This designation means the fire extinguisher can put out each of those types of fires. These are sometimes known as multipurpose fire extinguishers.
Your fire extinguisher has different substances inside, depending on its classification. For example, a Class A fire extinguisher contains pressurized water, while a Class D extinguisher has a dry, powdered form of sand or sodium chloride. Understanding the limitations and intended use of your extinguisher is crucial for eradicating fires quickly, safely and without accelerating the spread.
Fire Extinguisher Inspections
Fire extinguishers require regular checkups. If a status tag indicates that it has been five or more years since its last inspection — or if there are no recorded reviews — have the extinguisher reviewed and charged by a professional immediately.
The following are the four types of inspections fire extinguishers must regularly undergo to remain safe and effective.
Annual Inspections
All extinguishers should have a thorough inspection by a certified technician once each year. This examination verifies that the extinguisher is in good condition, is up to date on any necessary service — internal inspections, hydrostatic tests, etc. — and is compliant with applicable codes and standards.
Regarding annual inspections, the tag should distinctly list the following information:
- The inspecting company’s name and contact information
- The inspecting technician’s extinguisher certification or license number
- The fire extinguisher’s chemical type indicated via hole-punch
- Validation of inspection indicated via a hole-punch under “Serviced”
- A hole-punch indicating the month and year in which the inspector completed their checks, which is valid for one year from the date indicated
It is advisable to keep a separate record log to track all annual inspections, so you know when to schedule the next one. Record logs are also an excellent way to back up the information for your records, should something happen to the tag.
Monthly Inspections
The business owner or a designated representative should perform routine inspections on all a location’s extinguishers on no less than a monthly basis. This examination is a quick once-over to ensure that the extinguisher looks to be in good working order.
Regarding monthly inspections, verify the following information and record it accordingly:
- The extinguisher is in its designated place, unobstructed and mounted properly.
- There is no damage or any other condition that may prevent it from working correctly.
- The extinguisher’s pressure gauge reads in the green zone and has the proper charge, if applicable. Please note, CO2-type extinguishers do not have a pressure gauge.
- The fire extinguisher tag is present and indicates that the extinguisher is up to date regarding all inspections and required servicing.
Located on the rear of each fire extinguisher tag is a section for the date and initials of the on-site representative or business owner who performed the monthly inspection. In cases where the extinguisher tag does not have a designated space to document monthly inspections, you can use any blank space available.
Six-Year Inspections/5 year on CO2, Wet Agent, Stored Pressure Water, AFFF and FFFP
Every six years, empty your fire extinguisher and have it carefully examined by a licensed professional. During the six-year inspection, a trained tech will inspect the empty extinguisher for functioning, up-to-date mechanics and an intact outlet hose and delivery system. When they finish the examination, they will then refill, repressurize and mark the extinguisher with a 6-year interval examination label.
Each extinguisher that has undergone maintenance that includes the internal examination, except for cartridge and cylinder operated extinguishers, shall have a verification of service collar located around the neck of the container.
Hydrostatic Testing
The final type of inspection required for all portable fire extinguishers is hydrostatic testing, which refers to a process where a certified technician checks all critical areas of the extinguisher for any faults or defects using a specific type of pressurized liquid.
During a standard hydrostatic test, the technician will:
- Conduct a visual inspection of the valve and interior of the extinguisher.
- Secure the extinguisher in a steel chamber.
- Fill the steel chamber with water and record the current pressure level.
- Apply a high-pressure flow of water to the exterior of the extinguisher and record how it responds.
- List the extinguisher as either having passed or failed the hydrostatic test.
The frequency of required hydrostatic testing depends on the type of extinguisher in question, but it is always either every five or 12 years. The exception is any time an extinguisher has visual damage present, such as corrosion or distortion or after fire exposure.
After each passed hydrostatic test, the inspector should record the following information on the tag:
- The name and signature of the person or agency who performed the test
- The date the hydrostatic test took place
- The serial number or other identifiers of the fire extinguisher in question
Additional Areas to Inspect
In addition to annual, monthly and six-year inspections, there are a few other crucial areas of your fire extinguisher you should examine regularly.
- The exterior: During your regular visual inspections, check that the outside of your fire extinguisher — including the cylinder, handle and nozzle — is free of dents, puncture holes, warping, rust and corrosion.
- The safety pin: The safety pin is at the top of your fire extinguisher. Make sure it is securely in place, and free of damage or buildup.
- The instruction label: Every fire extinguisher should have a plainly marked instruction label on the side of the unit for easy access during emergencies. During your inspection, make sure this label is legible and intact. If it is peeling, faded or otherwise impossible to read in its entirety, replace your fire extinguisher.
- The location of the extinguisher: You should always be able to locate your fire extinguisher underneath an official fire extinguisher sign or similar indicator. Make sure the extinguisher is not difficult to see or obscured by nearby objects. Remember, easy access to your fire extinguisher is crucial for eradicating a fire quickly.
Regular fire extinguisher maintenance is essential. Do not use your fire extinguisher if it is noticeably damaged in any way. In doing so, you could risk worsening the fire, as well as causing injury to yourself and others. If you have concerns or questions about your fire extinguisher, contact a professional.
Telgian: The Fire Extinguisher Inspection Experts
Since 1985, Telgian has served as a trusted partner to clients around the globe, providing innovative solutions and keeping facilities safe, compliant and on budget. Telgian’s expertise includes testing, inspections and repair of fire extinguishers, as well as other fire life safety systems, including fire sprinkler systems, fire alarm systems, kitchen hood suppression systems, backflow systems, emergency/exit lights, special hazards, clean agent systems and fire alarm monitoring.
Telgian offers unparalleled experience. Our technicians perform inspections and tests at approximately 50,000 locations annually throughout the U.S. and Canada, including all types of fire extinguishers based on jurisdictional requirements.
To learn more about our Telgian fire and life safety testing, fire extinguisher inspections and repair services, reach out to us online or call us at 877-TELGIAN.
Last updated April 16, 2021.